Wx Python from scratch
Dialogs
In previous lessonings we have seen how to construct a GUI application by creating its individual elements. A Dialog is a pre-fabricated screen that can be implemented within a GUI application.
In this lessoning we will see, firstly, how to use a simple pop-up dialog, and then look in some more detail at a more powerful dialog: the file open dialog.
A simple message dialog
In order to demonstrate the use of a dialog, I will take the simple case of asking the user to confirm that they wish to close the frame. (I should say that it is considered good practise not to use this sort of dialog as they often annoy users … “Are you sure?” … “Are you really sure?” … “Are you absolutely sure?” …)
I will use the basic frame as a starting point, and bind the frame’s close event to a method:
import wx
class MainFrame(wx.Frame):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super(MainFrame, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.Bind(wx.EVT_CLOSE, self.on_quit_click)
self.Show()
def on_quit_click(self, event):
print("Now closing")
quit()
if __name__ == "__main__":
screen_app = wx.App()
main_frame = MainFrame(parent=None, title="Warning dialog")
screen_app.MainLoop()
Note that I have had to include a quit command in the close event as the method ‘captures’ the event and does not allow the quit to pass to the operating system.
Let us assume that we wish the user to confirm that they really did wish to close the frame. To implement this we need to insert a call to the dialog in the on_quit_click method:
def on_quit_click(self, event):
warning_dialog = wx.MessageDialog(self, message="Quit frame?",
style=wx.ICON_QUESTION|wx.YES_NO)
result = warning_dialog.ShowModal()
if result == wx.ID_YES:
print("Now closing")
quit()
This is a MessageDialog. Note that:
- the style flags enable us to define the icon and the buttons that will be utilised;
- the dialog is shown in Modal mode. This means that neither the main frame, nor any of its widgets, can be accessed while the dialog is open;
- the dialog returns a value which we can test before deciding what further action to take.
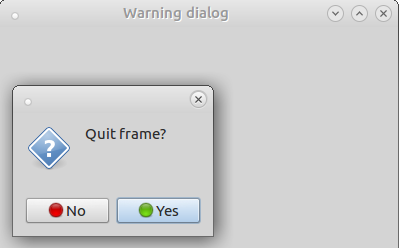
Fig 1. A warning dialog
The full code for this application can be found at warning_dialog.py.
The file open dialog
The file dialog uses a similar structure, but performs a more specific task. It is used when we want the user to select a file from the system.
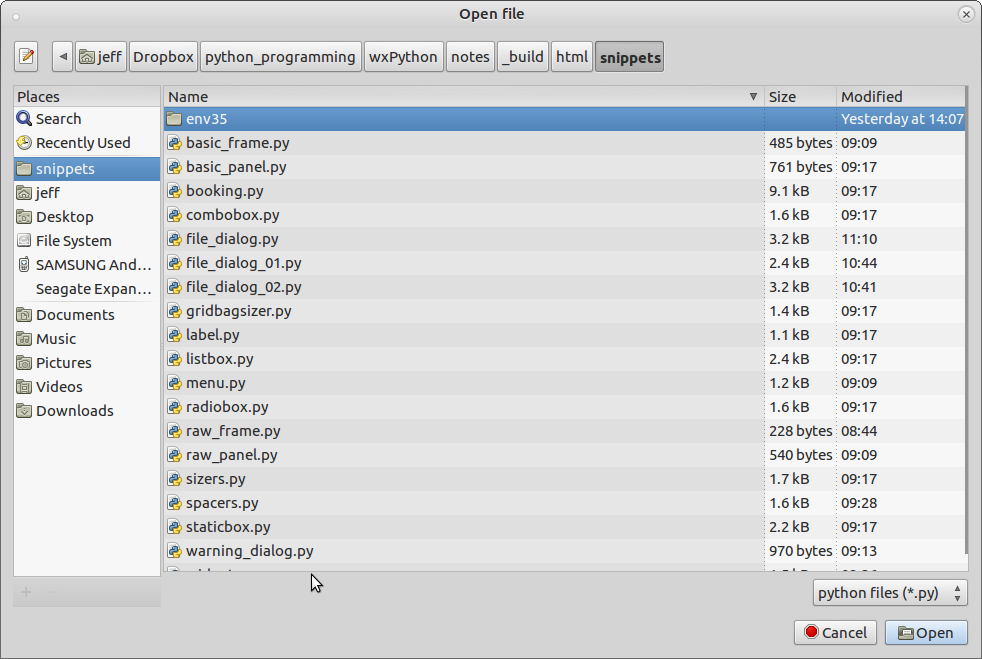
Fig 2. A file open dialog
‘File open’ is a slight misnomer: it does not open a file, but rather returns the path to a file. In the following example, I will use the dialog to retrieve a path and place it in text box. First I will show the code for the application before we add the dialog:
import wx
import os
class MainFrame(wx.Frame):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
"""Initialise the MainFrame class."""
super(MainFrame, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
panel = MainPanel(self)
sizer = wx.BoxSizer(orient=wx.VERTICAL)
sizer.Add(panel)
self.SetSizerAndFit(sizer)
self.Show()
class MainPanel(wx.Panel):
def __init__(self, parent, *args, **kwargs):
super(MainPanel, self).__init__(parent, *args, **kwargs)
self.path = "/home/jeff/"
path_sizer = self.create_path_sizer()
button_sizer = self.create_button_sizer()
sizer = wx.BoxSizer(orient=wx.VERTICAL)
sizer.Add(path_sizer, flag=wx.ALL, border=10)
sizer.Add(button_sizer, flag=wx.LEFT|wx.RIGHT|wx.BOTTOM|wx.EXPAND, border=10)
self.SetSizer(sizer)
def on_cmd_path_click(self, event):
del event
def on_cmd_quit_click(self, event):
del event
quit()
def create_path_sizer(self):
lbl_path = wx.StaticText(parent=self, label="Path:")
self.txt_path = wx.TextCtrl(parent=self, size=(300, -1))
cmd_path = wx.Button(parent=self, id=wx.ID_OPEN)
cmd_path.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.on_cmd_path_click)
sizer = wx.BoxSizer(orient=wx.HORIZONTAL)
sizer.Add(lbl_path, flag=wx.RIGHT, border=10)
sizer.Add(self.txt_path, flag=wx.RIGHT, border=10)
sizer.Add(cmd_path)
return sizer
def create_button_sizer(self):
cmd_quit = wx.Button(parent=self, id=wx.ID_EXIT)
cmd_quit.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.on_cmd_quit_click)
sizer = wx.BoxSizer(orient=wx.HORIZONTAL)
sizer.Add((0, 0), proportion=1)
sizer.Add(cmd_quit)
return sizer
if __name__ == "__main__
screen_app = wx.App()
main_frame = MainFrame(parent=None, title="Open file dialog")
screen_app.MainLoop()
This contains only elements that we have seen before. I have imported os because this will be required later. The panel has a sizer to hold the path widgets: a label, a textbox and a button; and a sizer to hold the Quit button.
The code to invoke the file open dialog and place the selected path in the txt_path text box is:
def on_cmd_path_click(self, event):
del event
self.path = self.get_file_path()
self.txt_path.SetValue(self.path)
and the get_file_path function:
def get_file_path(self):
path = self.path
file_types = "python files (*.py)|*.py|All files (*.*)|*.*"
file_dialog = wx.FileDialog(parent=self,
message = 'Open file',
defaultDir=os.path.dirname(path),
defaultFile=os.path.basename(path),
wildcard=file_types,
style=wx.FD_OPEN)
if file_dialog.ShowModal() == wx.ID_OK:
path = file_dialog.GetPath()
file_dialog.Destroy()
return path
This code (file_dialog.py) should be self explanatory except for the file_types string which is assigned to the wildcard argument. The string is delimited by the pipe character (“|”). The delimited strings must be taken in pairs. So, if we look at the pair “python files (.py)|.py”, the first element (“python files (.py)”) is the string that will appear in the select file combobox in the dialog and the second (“.py**“)is the wildcard that will be applied when the selection is made.
The style argument defines the behaviour of the dialog and which buttons will appear. A similar dialog can be created for saving files using the style FD_SAVE.
Summary
In this lesson I have described the use of two of the wxPython dialogs. The next lesson will deal with two important controls: the Date Picker control, used for selecting a date, and the ObjectListView used for displaying data in a list format.